Athena Skin Hair & Dental Clinic
Seborrheic Dermatitis
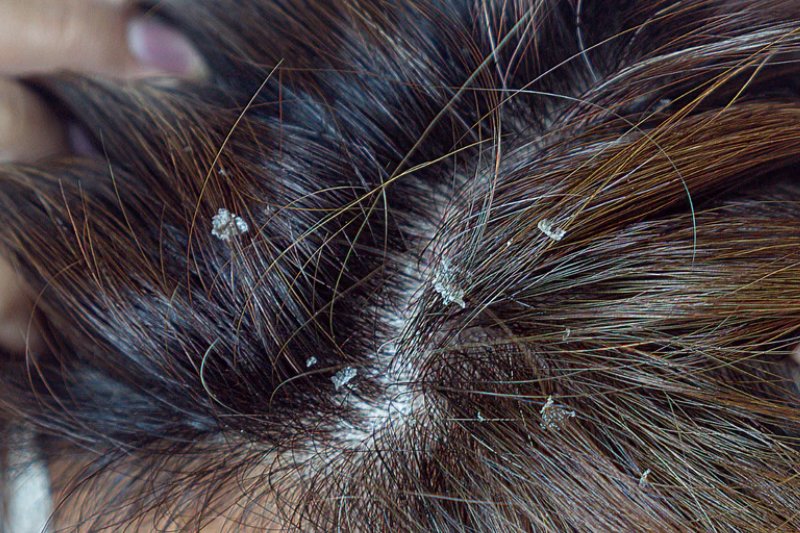
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common, chronic skin condition that primarily affects areas of the body with a high density of sebaceous (oil) glands, such as the scalp, face, chest, and back. It is characterize by red, scaly, and often itchy patches on the skin. The exact cause of It is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, environmental, and fungal factors.
It is a chronic condition, which means that even though symptoms may be manage or alleviate, they can recur periodically. Long-term management and symptom control are often necessary.When It treatment occurs on the scalp, it is commonly refer to as dandruff. Dandruff results in flaky, itchy, and sometimes oily or greasy skin on the scalp.
Causes of seborrheic dermatitis
Genetic Predisposition: It tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition. If you have close relatives with the condition, you may be more likely to develop it.
Hormonal Factors: Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during puberty, pregnancy, or in some medical conditions, can influence the development or exacerbation . Hormonal fluctuations may increase the production of skin oils, contributing to the condition.
Environmental and Weather Conditions: It is often more prevalent in areas with cold, dry climates. Changes in weather, particularly during the winter months, can lead to flare-ups of the condition.
Stress: High levels of stress or emotional tension may contribute to or exacerbate seborrheic dermatitis. Stress can affect the body’s immune response and lead to changes in skin health.
Skincare and Haircare Products: The use of certain skincare or haircare products, especially those that contain harsh or irritating ingredients, can trigger or worsen seborrheic dermatitis. This includes shampoos, hair gels, and makeup.
treating seborrheic dermatitis
Topical Antifungal Agents:
- Over-the-Counter Shampoos: Medicate shampoos containing active ingredients like ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, or zinc pyrithione can be use to treat scalp (dandruff). These shampoos are applied according to the product instructions and left on the scalp for a specific period before rinsing.
- Topical Creams or Lotions: For facial or body seborrheic dermatitis, topical creams or lotions containing antifungal agents, such as ketoconazole, may be recommended. These should be applied as direct by a healthcare provider.
Topical Corticosteroids:
- Low-Potency Corticosteroids: For inflammation and itching associate with seborrheic dermatitis, low-potency topical corticosteroids can help reduce symptoms. These should be use sparingly and as direct by a healthcare provider.
Coal Tar Preparations:
- Coal tar-base products can be use to alleviate symptoms and reduce inflammation in some cases. These are available in various forms, such as shampoos, creams, and ointments.
Prescription Medications:
- In cases of severe or persistent seborrheic dermatitis, a healthcare provider may prescribe stronger topical antifungals, corticosteroids, or combination products. These should be use under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
What are the Types?
Scalp (Dandruff): This is the most common type and typically affects the scalp. It often results in flaky, itchy, and sometimes oily or greasy skin on the scalp. It is commonly refer to as dandruff.
Facial: This type affects the face and is characterize by red, scaly, and often itchy patches. It frequently appears in areas with a high concentration of sebaceous glands, such as the eyebrows, eyelids, and creases around the nose. In infants, this is known as “cradle cap.”
Genital: Although less common, It can affect the genital area. It may lead to redness, itching, and scaling in the genital region. In men, it can involve the scrotum, while in women, it may affect the vulva.
Infantile (Cradle Cap): This type affects infants and is characterize by thick, yellow, or greasy scales on the scalp. It typically does not cause itching or discomfort and tends to resolve on its own.
risk factors
Age: It often begins in infancy (cradle cap) and is more common in adults between the ages of 30 and 60. It can occur at any age but tends to be more prevalent in certain life stages.
Family History: Individuals with a family history of seborrheic dermatitis are more likely to develop the condition, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
Neurological Factors: Some researchers believe that neurological factors, such as changes in nerve function or neurolog
